The introduction of eSIM and remote SIM provisioning (RSP) has opened new opportunities for telecom service providers (SPs) to fully digitalise their services. By allowing SPs to remotely program subscriber profiles, RSP eliminates needing a physical SIM card to authenticate the service. This advancement not only streamlines operations for telecom companies but also enables companies outside the telecom industry to leverage and capitalise on eSIM.
In this blog, we’ll explain remote SIM provisioning and how it works and explore the current remote SIM provisioning options available for the consumer market.
TL;DR
- Remote SIM provisioning allows SIM cards to be activated and managed remotely without the need for physical swapping.
- This technology offers the following for consumers and businesses while reshaping the telecom industry’s landscape:
- Convenience
- Flexibility
- Security
- Scalability
What is remote SIM provisioning?
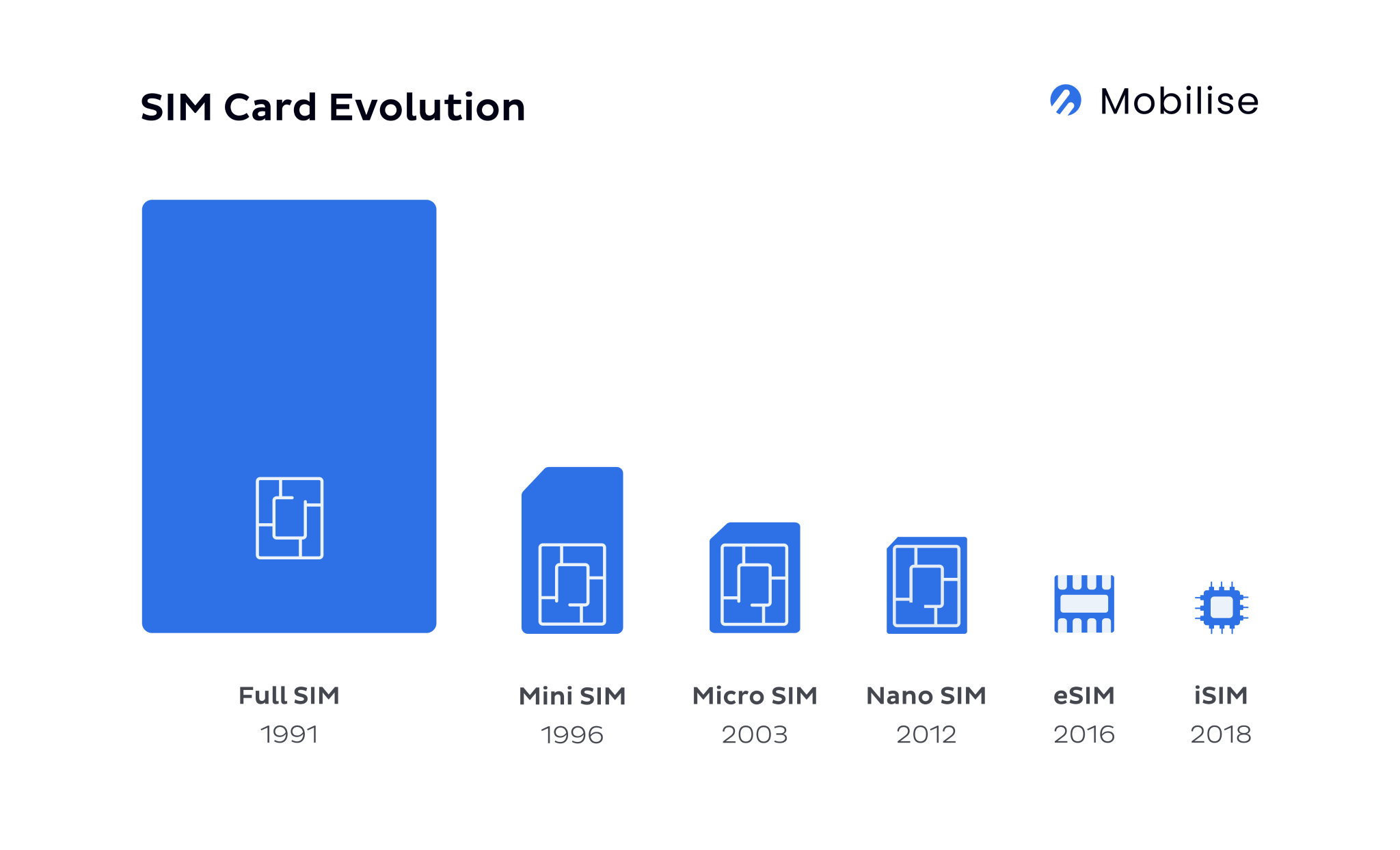
Remote SIM provisioning is an over-the-air process of eSIM profile management. It includes eSIM authentication and activation, enabling, disabling, and deleting.
Since 1991, a removable plastic SIM card has been the only way to authenticate mobile devices. SIM cards would have authentication parameters, such as international mobile subscriber identity (IMSI) numbers and the key (Ki), pre-programmed on them. Those parameters couldn’t be changed or deleted. Therefore, if a user wanted a new phone number, they had to remove the old SIM card and pop a new one into their device.
RECOMMENDED READING
How does remote SIM provisioning work?
eSIMs have the same function as plastic SIM cards; however, they work slightly differently.
There are 2 primary elements that make an eSIM:
- The embedded universal integrated circuit card (eUICC), often called an eSIM chip that’s soldered within the device.
- And an eSIM profile, which is a digital version of the authentication parameters.
Some may get confused with the terms eUICC vs eSIM but the main difference between them is that eUICC is a part of eSIM and not the full eSIM ecosystem.
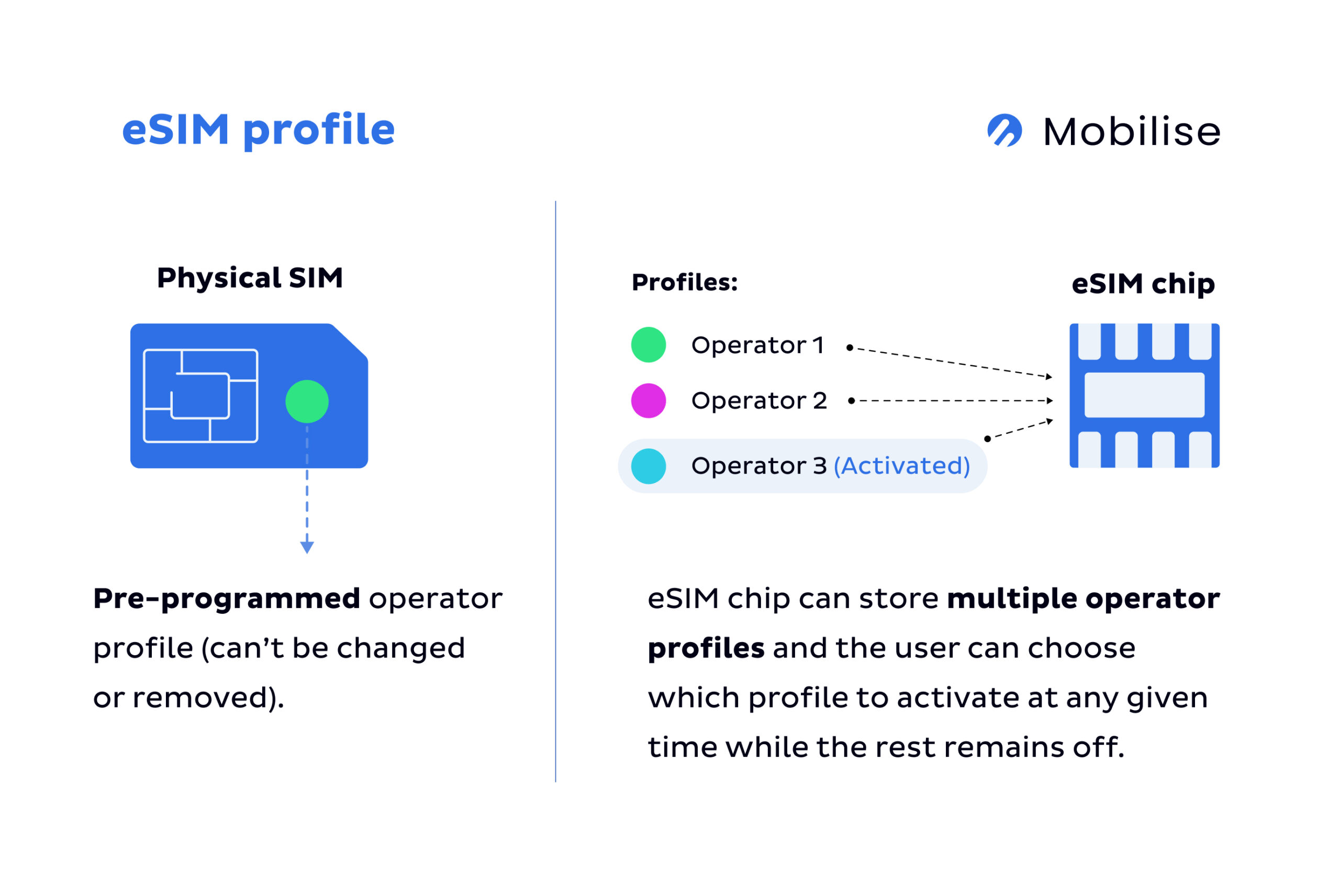
The remote SIM provisioning process enables users to download the eSIM profile into the eUICC on their device and activate their subscription. It’s also used for other functions like switching between the profiles or deleting them. There are a few ways of enabling eSIM on a consumer device, we’ll outline them in the next section.
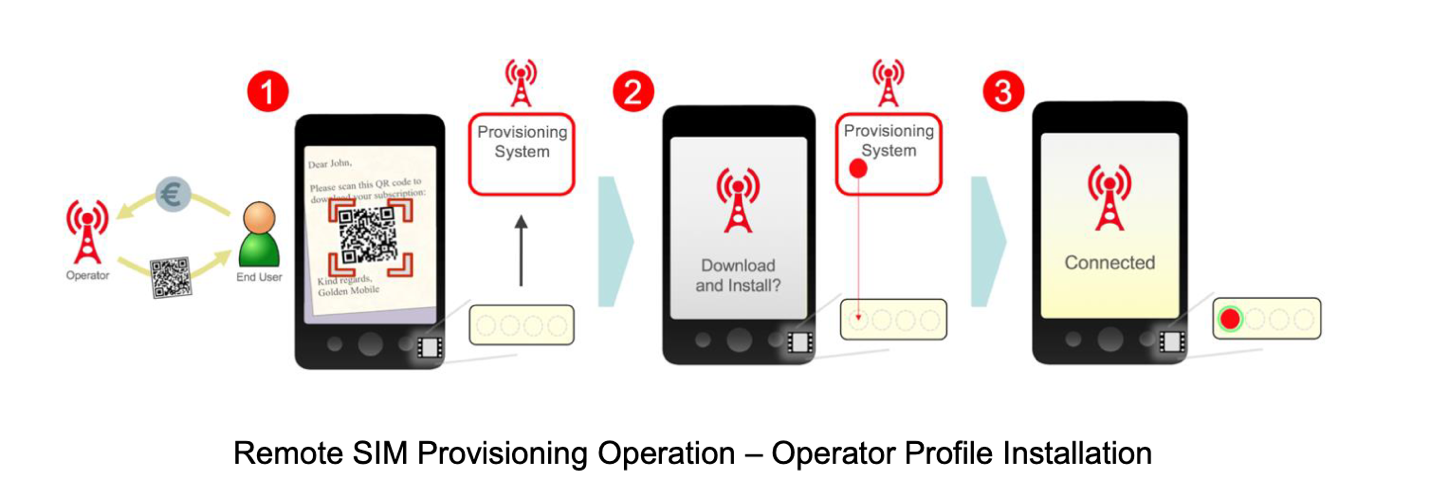
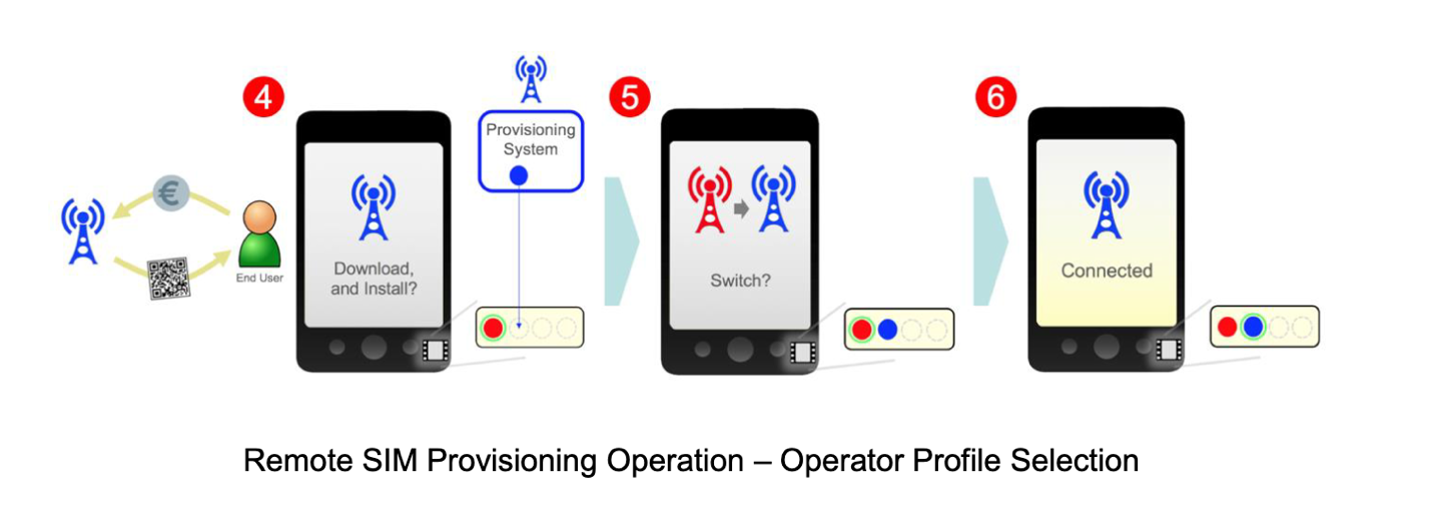 Source: eSIM Whitepaper by GSMA
Source: eSIM Whitepaper by GSMA
Types of eSIM provisioning
There are currently several methods to provision an eSIM, which we’ll go into more detail here:
In-app eSIM provisioning
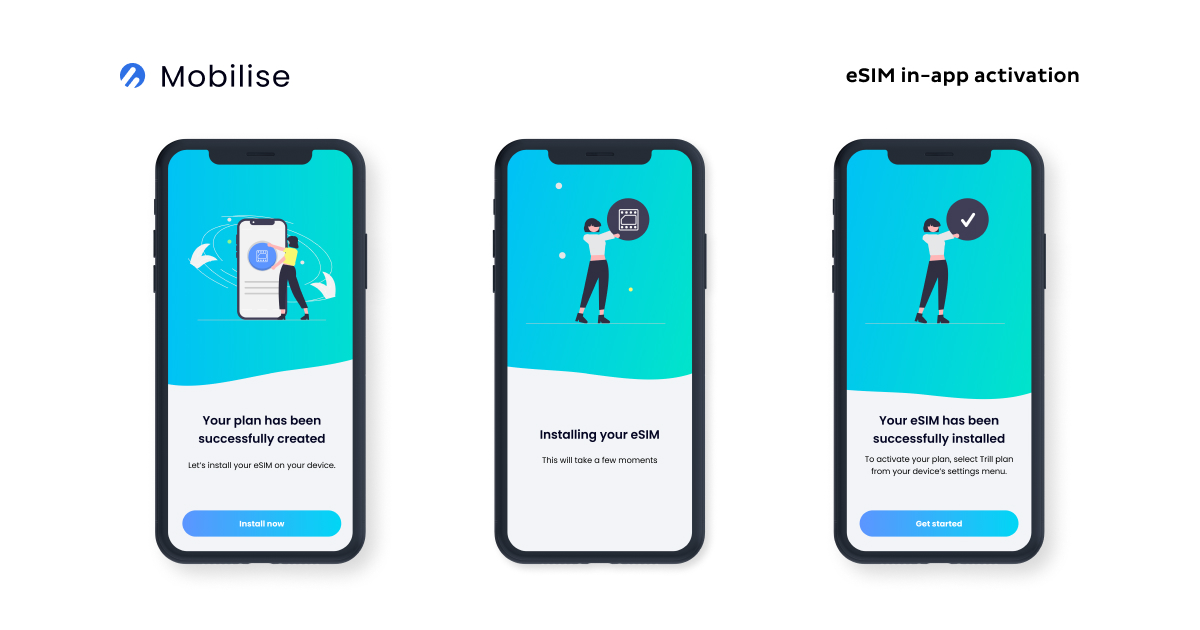
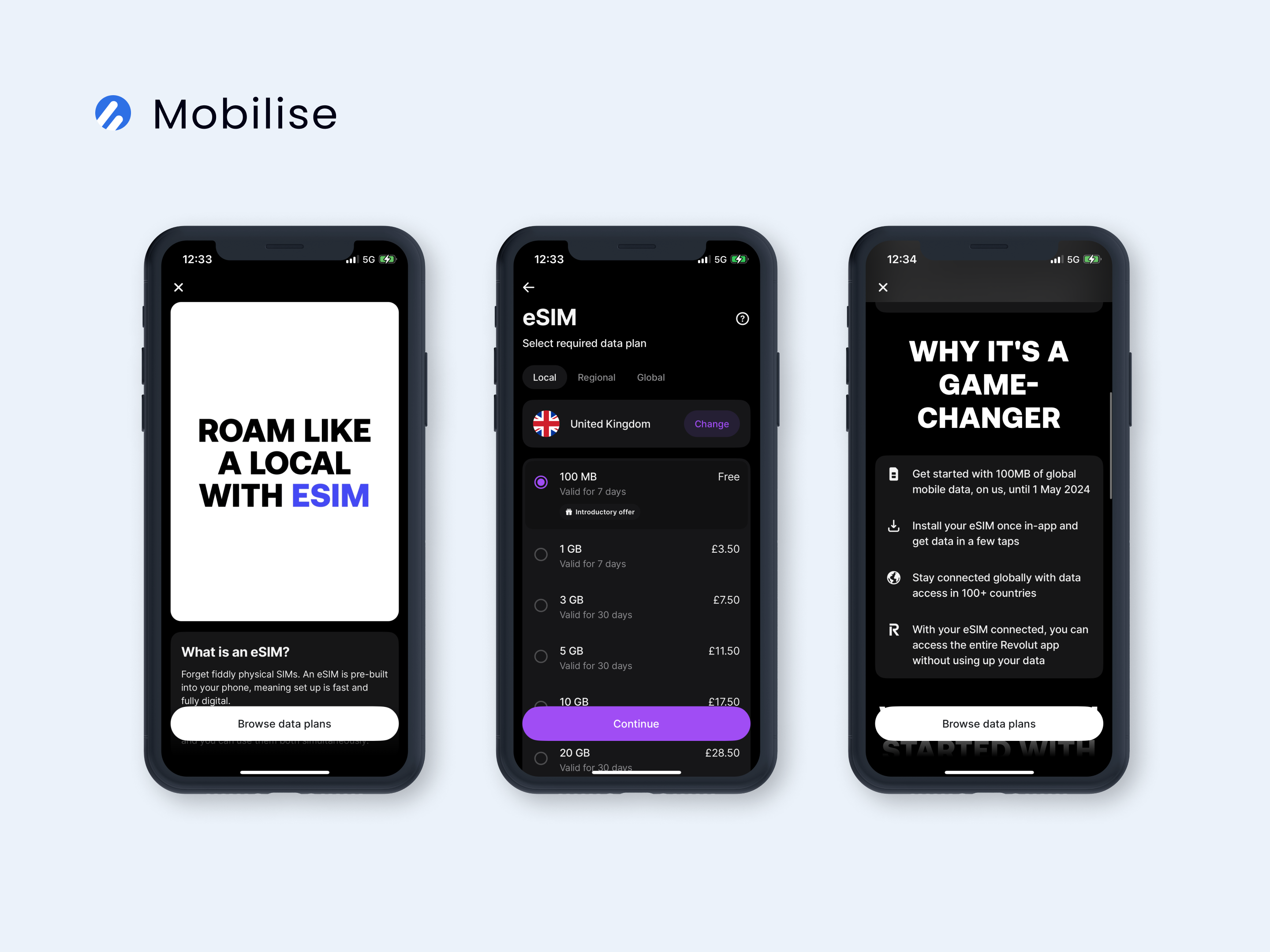
One of the most efficient methods for remote SIM provisioning is in-app eSIM activation. It’s fast, straightforward, and user-friendly. Users simply download the operator’s mobile app, choose their data bundle or subscription plan, and activate their eSIM profile with a single tap. It takes up to 60 seconds for the eSIM profile to activate.
How does it work, you might ask? Well, this is because the mobile app interacts directly with the device’s operating system APIs, passing the SM-DP+ information to the eUICC chip embedded in the device. This capability allows the app to seamlessly activate, delete, and manage eSIM profiles on the device.
Mobilise’s eSIM solutions, such as eSIM as a Service and the Embedded Connectivity SDK, utilise in-app eSIM activation to offer a smooth and quick onboarding experience. The intuitive nature of in-app activation eliminates the need for complex visual explanations or step-by-step instructions, making it the preferred choice not only for us but also for many users.
QR codes
This method leverages the familiarity and simplicity of QR codes. Upon purchasing an eSIM, users receive a QR code via email, which contains the address of the remote SIM provisioning system (SM-DP+).
By scanning the QR code, the device connects to the system and securely downloads the SIM profile. QR code activation is generally easier and more accessible than manual activation, making it suitable for less tech-savvy users.
However, it requires access to another device or a printer to display or print the QR code for scanning, adding an extra step to the onboarding process.
 Source: Digital Trends
Source: Digital Trends
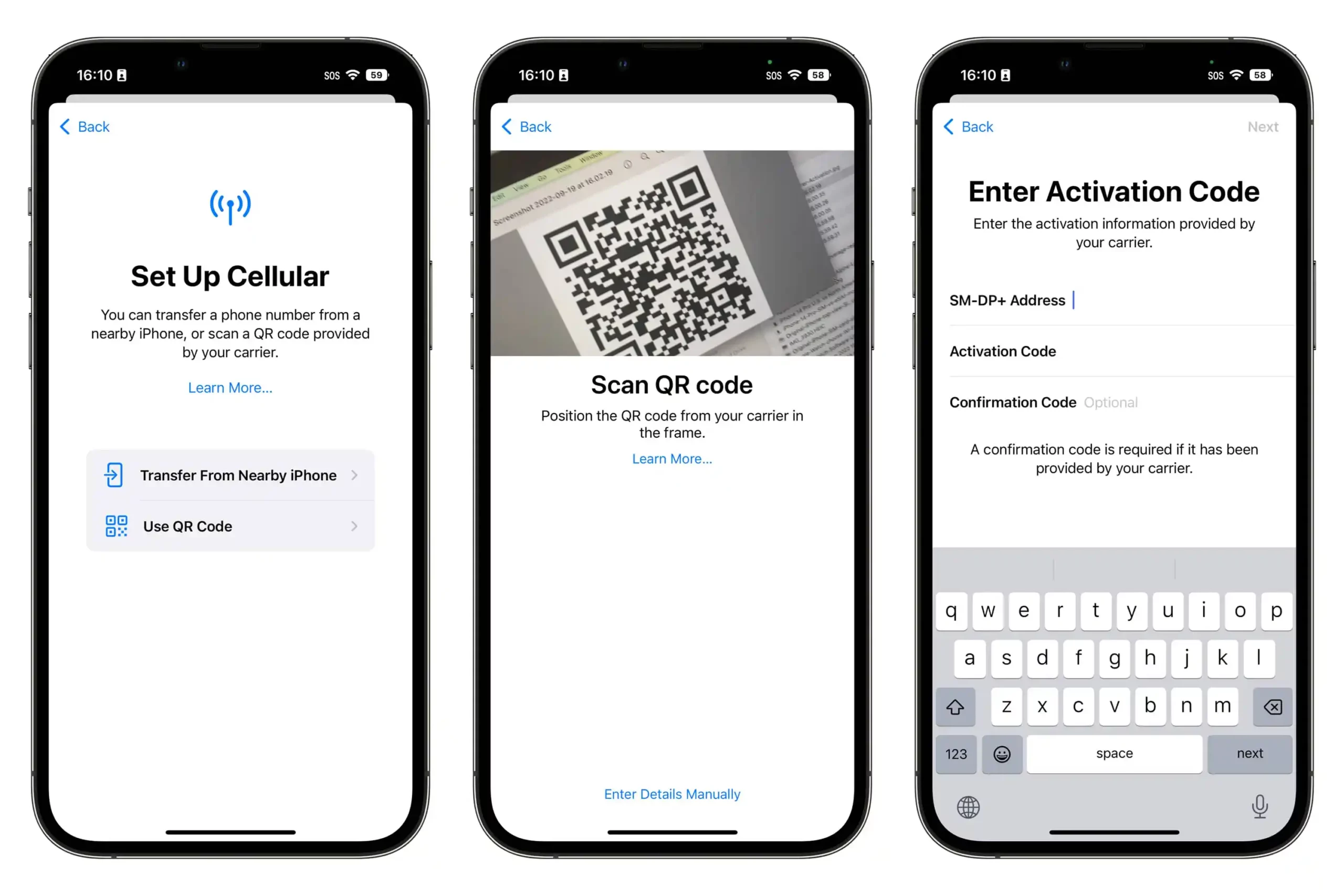
Manual eSIM activation
This method of activating an eSIM is more technical and less user-friendly, often serving as a fallback option when other activation methods are unavailable or fail. For instance, it’s useful when a user lacks access to another device or a printed QR code.
To manually activate an eSIM, users must obtain the SM-DP+ address and an activation code from their SP, typically sent via email. The activation steps can vary between iOS and Android devices and may differ further based on the specific device model.
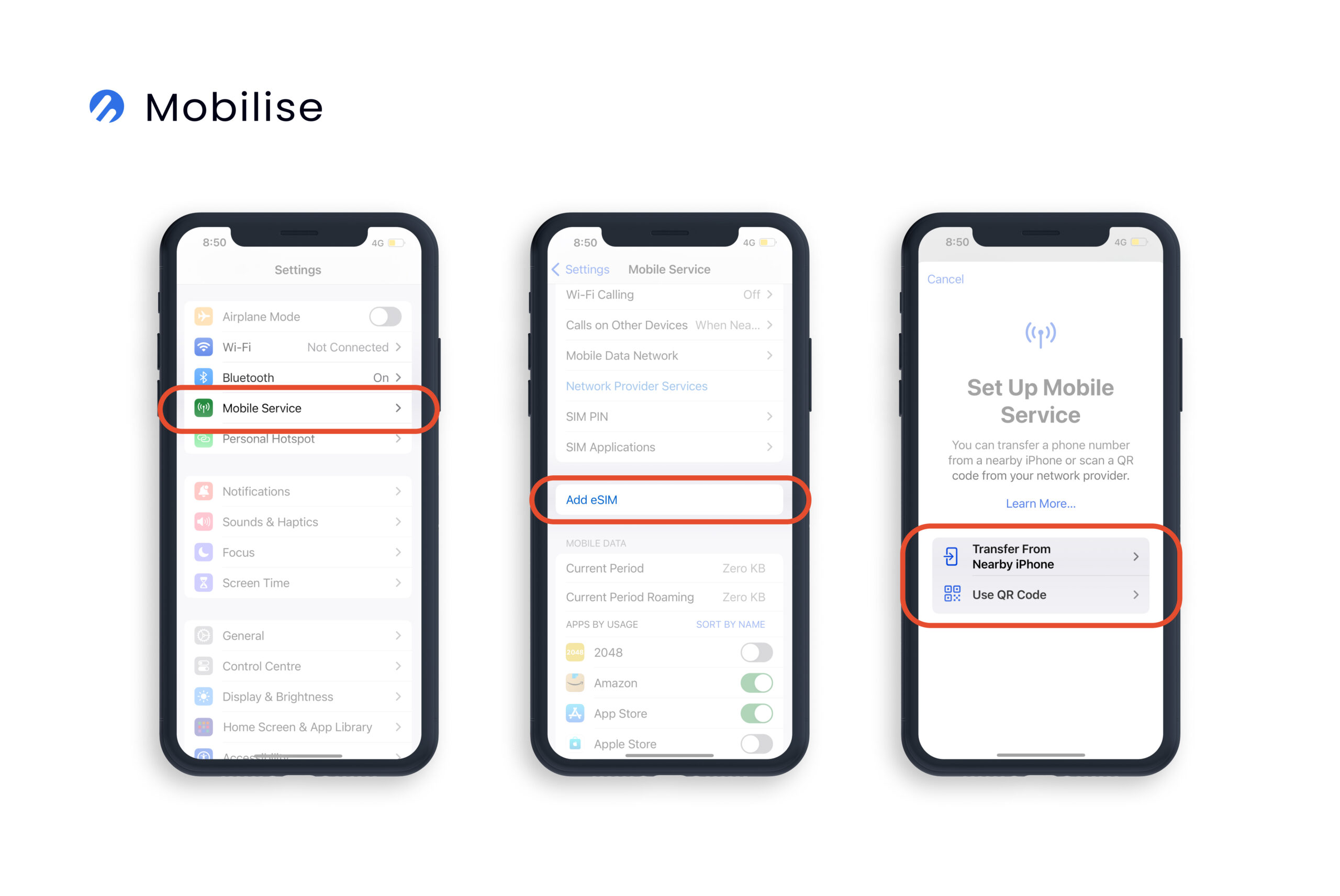
- iOS (iPhone 13 Mini): A user needs to go to Settings > Mobile Service > Add Data Plan or Add eSIM > Use QR Code > Enter Details Manually. That’s where they need to type the received SM-DP+ address, activation code and, optionally, a confirmation code.
- Android (Samsung Galaxy S21 5G): A user needs to open the device settings and follow this process: Settings > Connections > SIM Card Manager > Add a Mobile Plan > Scan Carrier QR Code > Enter Activation Code and input the SM-DP+ address and activation code.
We don’t recommend offering manual eSIM activation as the primary/only option. It may confuse less tech-savvy consumers and discourage them from using eSIM.
Benefits of remote SIM provisioning
eSIM is set to become the standard of SIMs. The global size of the eSIM market was approximately USD 8.34 billion in 2022, and it’s estimated to reach USD 19.35 billion by 2031.
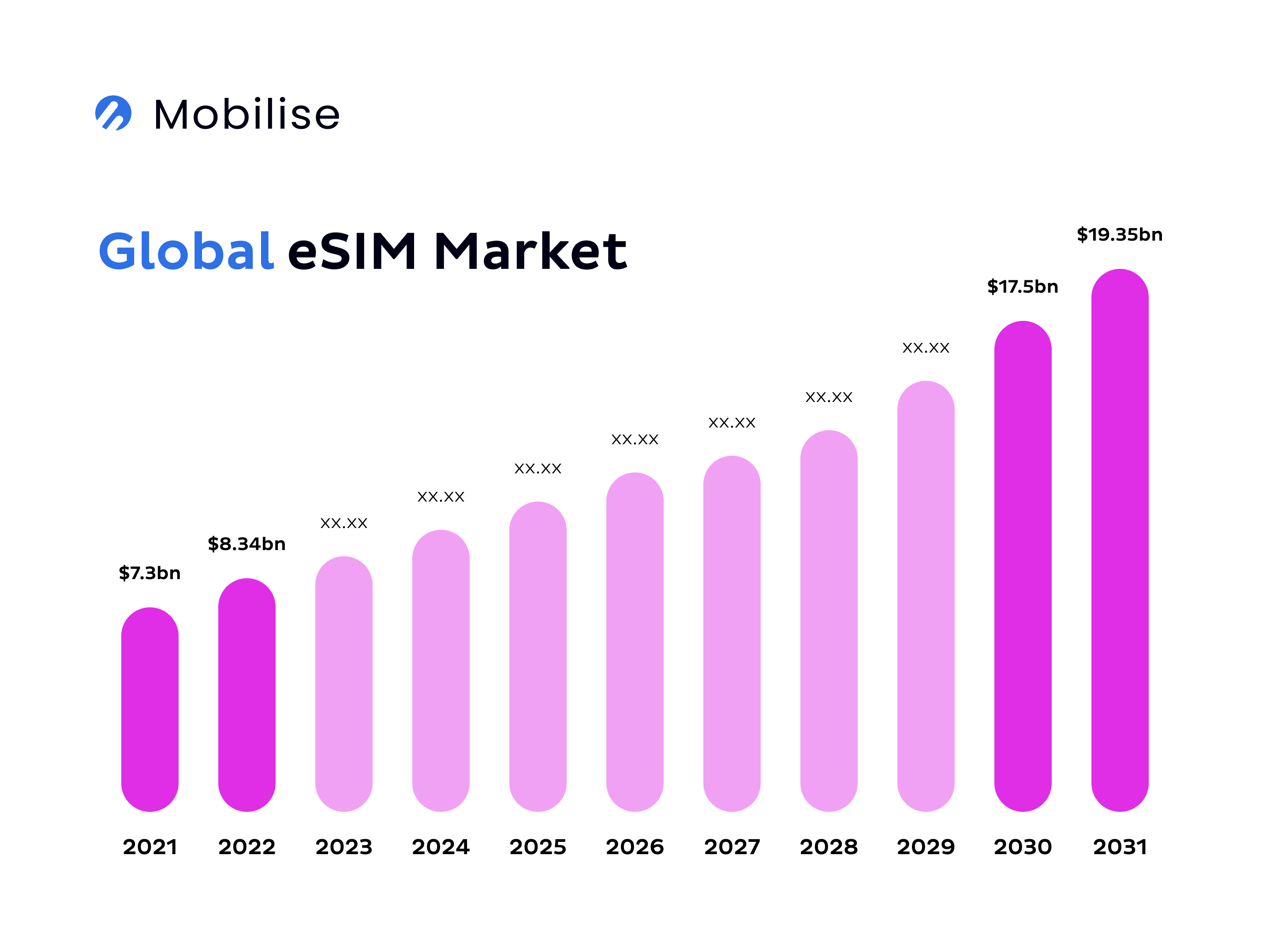 Source: Mobilise, based on Straits Research
Source: Mobilise, based on Straits Research
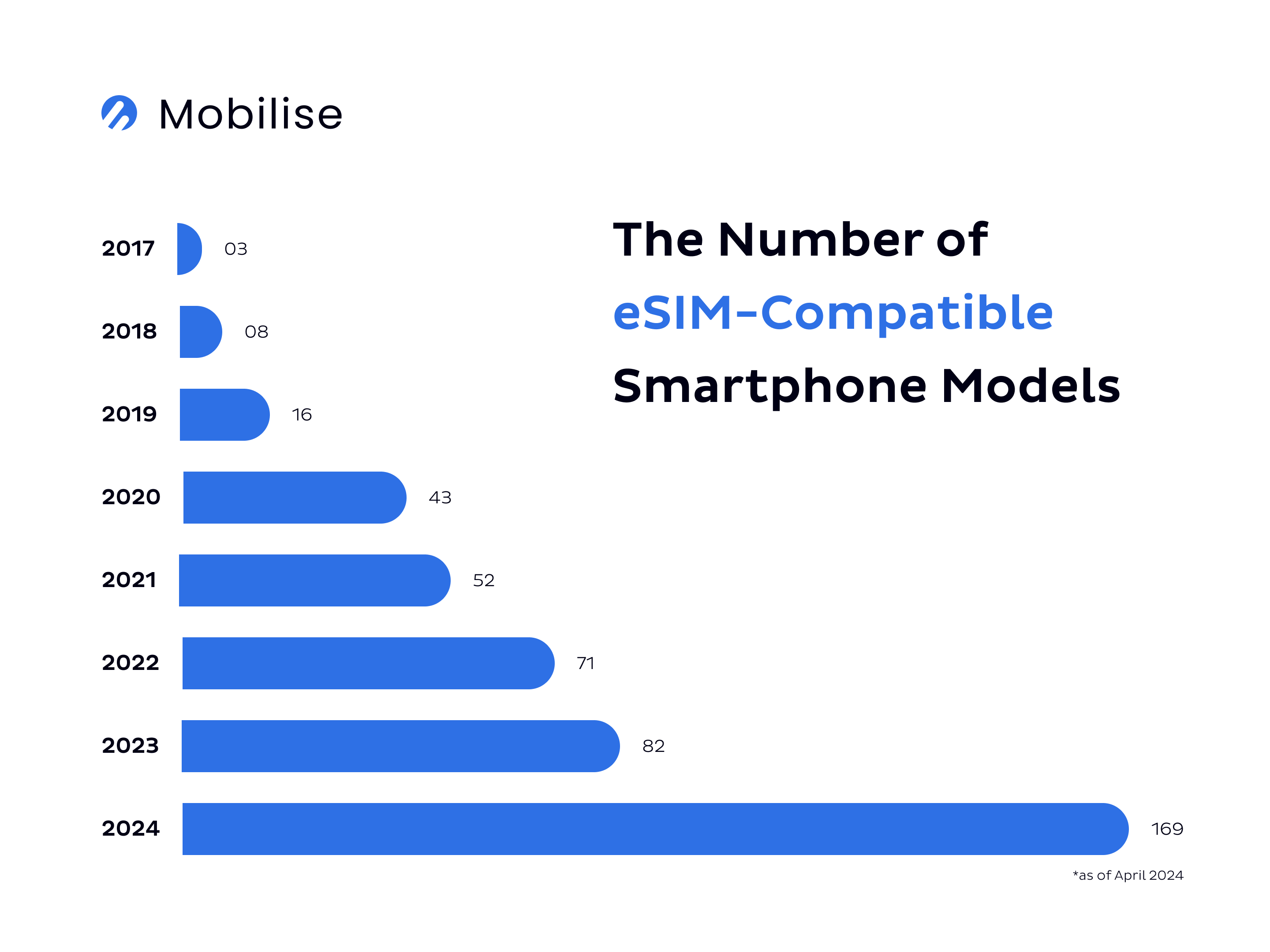 Source: Mobilise based on Holafly
Source: Mobilise based on Holafly
On top of that, as of April 2024, the number of eSIM-compatible smartphones increased to 169. eSIM implementation and remote SIM provisioning enables all those devices to use eSIMs which bring plenty of benefits for both consumers and service providers.
Convenience
RSP eliminates the need to physically swap SIM cards, making it easier for users to switch carriers or update their service plans. This is particularly beneficial for travellers who frequently change SIM cards to avoid roaming charges.
Increased flexibility
eSIMs can store multiple eSIM profiles at the same time, and remote SIM provisioning helps enable and disable eSIM profiles at will, so users can manage them across different networks or countries.
Enhanced security
Remote SIM provisioning is an over-the-air process which decreases the possibility of theft of a SIM card and its credentials and use for malicious purposes. eSIM profiles are encrypted and can be remotely deactivated if a device is lost or stolen, providing an additional layer of protection in eSIM security.
Scalability
As the number of connected devices increases, remote SIM provisioning supports seamless and scalable connectivity management. This is critical for the mass adoption of eSIM, where devices must be easily and remotely managed.
Remote SIM provisioning impact on telecom industry
Remote SIM provisioning is causing telecom companies to reconsider their business models. Traditional SIM card logistics are becoming outdated, resulting in cost savings and improved operational efficiencies. On top of this, consumers are relying more and more on digital solutions that fit into their day-to-day lives.
Take, for example, the emergence of superapps in multiple industries. These apps include a number of different ancillary services to cater to the needs of the modern consumer within a single app. Revolut, a popular digital bank, offers eSIM data plans across more than 100 countries, perfect for frequent travellers. Customers can install an eSIM via the Revolut app and can easily top up as needed.
Currently, consumers perceive telco apps as utility tools but would prefer a single telco app with multiple and diverse functions and features. As a result, operators are now focused on offering more flexible and innovative service plans to attract and retain customers.
RSP is also changing the relationship between operators and customers. With easier switching between operators, customer loyalty is driven more by service quality and pricing than contractual obligations and physical SIM limitations.
Loyalty programmes, rewards, and referrals are all methods that telcos utilise to attract customer loyalty. But customer experience (CX) can make or break their loyalty. Remote SIM provisioning paired with in-app eSIM activation provides a more straightforward and user-friendly approach that can keep a user coming back for more. In fact, a successful onboarding process would increase 46% of consumers’ likelihood of spending more on a product or service.
How to implement remote SIM provisioning?
At Mobilise, we’ve combined years of telecom expertise, software development experience and best UX principles to create a portfolio of eSIM solutions for every need. We cater to all types of requirements.
Our white-label eSIM app was created with SPs that don’t yet have an app store presence. With our Embedded Connectivity SDK, we can help companies from the telecoms industry and beyond to supercharge their existing mobile apps with eSIM functionality.

Both of our solutions come with in-app eSIM provisioning – the best and most user-friendly remote SIM provisioning option currently in the market. And we do all the heavy lifting so our clients can focus on their users and products.
Conclusion
Remote SIM provisioning is revolutionising mobile connectivity by enabling eSIM activation and management without physical SIM cards. This approach offers convenience, flexibility, security, and scalability for consumers and service providers alike. For telecom operators, it means reduced operational costs and delivering a fully digital experience. Non-telcos, like travel operators and the banking industry, can also tap into new revenue streams with RSP.
As eSIM and remote SIM provisioning continue to evolve, businesses should explore RSP further and consider the implementation of remotely activated eSIM solutions. If you’re interested in how Mobilise’s eSIM solutions can benefit your business, contact us today!